
For many years viruses have been known to be hazardous to man and can lead to outbreaks and pandemics. Some of these viruses are known for their high rate of transmission, immunopathogenicity and lethality and can cause severe disease or death in man. This article examines the history and effects of the 10 worst viral infections and ways through which they have been controled.
Contents
1. Marburg Virus
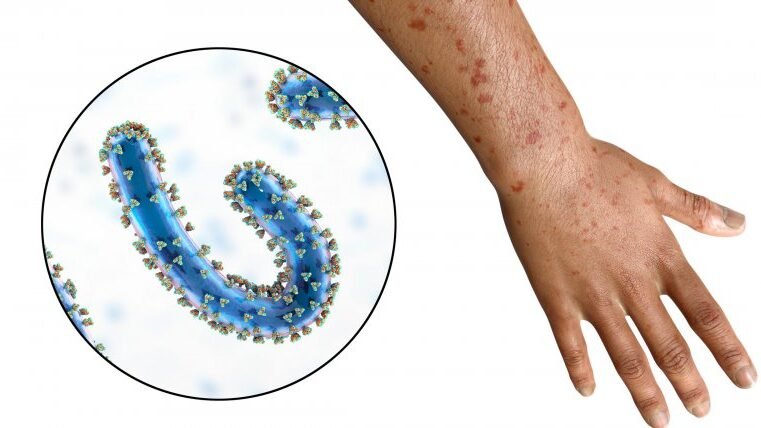
Overview
Marburg virus is a type of filovirus with similarity to the Ebola virus. It is responsible for Marburg Hemorrhagic Fever (MHF), which in man is severe and frequently fatal.
History
First described in 1967 in association with epidemics occurring in Germany and onwards to Yugoslavia also it was proven to have originated from infected monkeys used in experiments.
Symptoms
High fever
Severe headache
Vomiting blood
He presented with hemoptysis, massive hematemesis, melena, and hematuria; the patient was pale, cold sweated and cyanotic with thirst.
Fatality Rate
It has the potential to cause mortality rate of 88% depending with the type of outbreak and the ability of the patients to access treatment.
Notable Outbreaks
The epidemic in Angola between October 2004 and February 2005 produced more than 300 cases in which 90 % of the patients died.
2. Ebola Virus
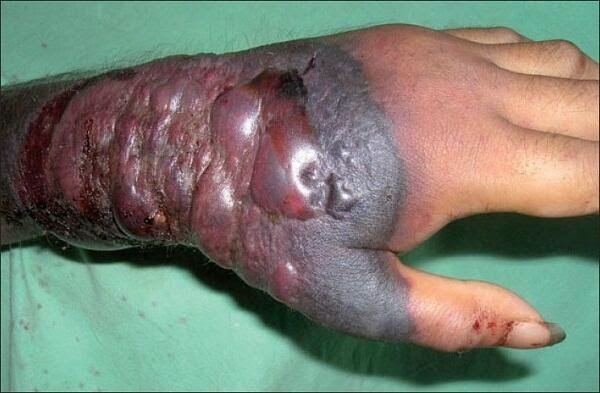
Overview
Another filovirus is the Ebola virus which leads to the virologic syndrome known as Ebola Virus Disease (EVD) with features of bleeding, multiple organ dysfunction and shock.
History
It was first detected in 1976 in the area of the Ebola River, in the Democratic Republic of Congo.
Symptoms
Fever and muscle pain
Vomiting and diarrhea
Uncontrolled bleeding
Fatality Rate
Mortality stands somewhere between 25% as well as 90% depending on the strain and treatment
Notable Outbreaks
The worst and latest which was the West Africa outbreak which started from 2014 to 2016 had killed over 11,000 people while more than 28,000 people were infected by the virus.
Prevention and Treatment
Other experimental products which include the rVSV-ZEBOV
Oxygen and simple care like fluids sucking
3. HIV (Human Immuno-deficiency Virus)
Overview
HIV attacks the body immune system, the CD4 cells and if not treated, results in AIDS.
History
Discovered as early as in 1983.
Transmission
Unprotected sex
Sharing needles
Mother-to-child transmission
Impact
HIV has killed more than 36 million people globally and 38 million people are living with this virus up to the year 2024.
Treatment
Although there is no cure for AIDS, Antiretroviral therapy makes it possible for AIDS patients to live long healthy lives like normal people.
4. Rabies Virus
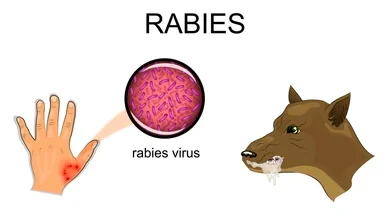
Overview
It is worth mentioning that rabies is nearly always fatal if the first signs are recognized, which puts it at the highest levels of virulence.
Transmission
Transmitted through the bite or scratch from infected animals including dogs, bats, raccoons and other.
Symptoms
Poor labeling key signals are anger or anxiety, confusion as well as aggression.
Hydrophobia (fear of water)
Paralysis leading to death
Fatality Rate
Almost 100 percent if they have not been treated before they show first signs of the disease.
Prevention
Human effective rabies vaccine and safe animal rabies vaccine
The following are classified under immediate PEP
5. Hantavirus
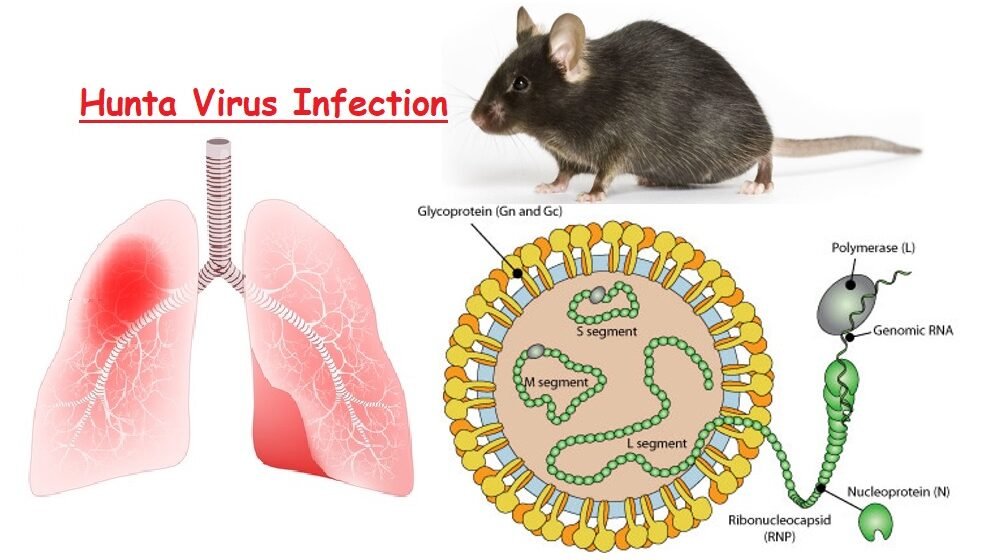
Overview
Hantavirus is responsible for a fatal lung syndrome known as Hantavirus Pulmonary Syndrome (HPS).
Transmission
Acquired by contact with rodent feces, urine, or saliva.
Symptoms
Fever and muscle aches Sneezing and difficulty in breathing Rapid respiratory failure
Fatality Rate
Up to 38% for HPS cases.
Notable Outbreak
The 1993 Four Corners outbreak in the United States brought this virus to public attention.
6. Influenza (Flu) Virus

Overview
Flu is an almost annual bug that occasionally produces particularly dangerous strains that can lead to pandemics.
Types
Seasonal Flu: Regular outbreaks every year Pandemic Flu: Worse ones such as the H1N1 and H5N1 strains
Fatality Rate
The mortality rate varies. Spanish flu (1918) had a mortality rate of 2.5% nevertheless it killed more than 50 million people.
Notable Pandemics
Spanish Flu (1918–1919): Over 500 million infected H1N1 (2009): As much less severe as the waves that form on water’s surface but it has infected millions of people all over the world.
Prevention
Annual flu vaccines This can be done in the form of antiviral chemicals like Tamiflu.
7. Dengue Virus
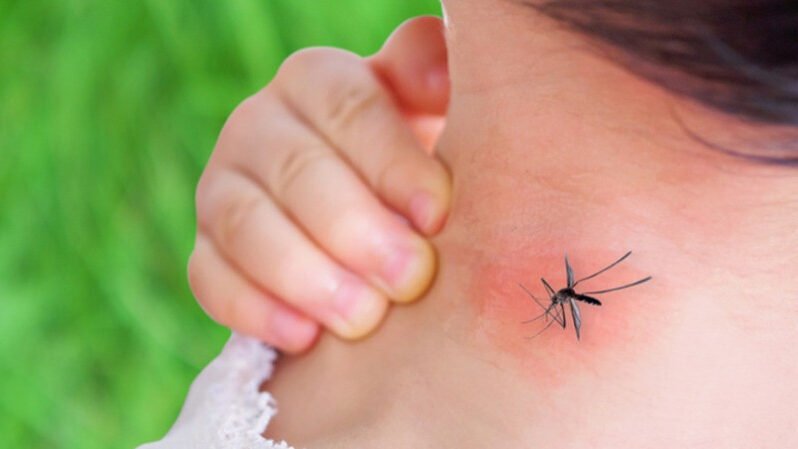

Overview
Er Victoria of the tropical regions and transmitted through the Aedes mosquitoes, which cause Dengue Fever.
Symptoms
Headache which is really severe and fever that increases up to very high levels.
Muscle and joint pain or breakbone fever
In its severe form the disease is referred to as Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever
Fatality Rate
Mortalities of severe cases under the condition that no treatment is administrated can be up to 20%.
Global Impact
There are more than 400 million new infections each year the majority of people, more than one in two people globally, are affected.
8. Smallpox Virus
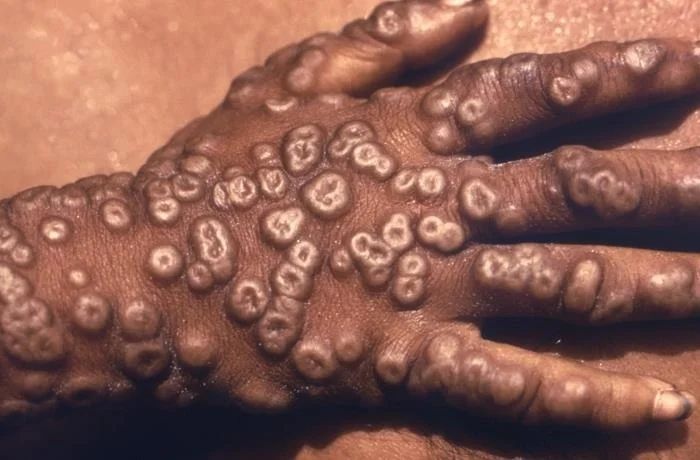
Overview
Small pox is one of the oldest and most fatal diseases which was declared extinct in 1980 but this is due to use of the vaccine.
Symptoms
High fever and fatigue
Characteristic pustular rash
Blindness in severe cases
Fatality Rate
Up to 30% during outbreaks.
Impact
Smallpox killed between 300–500 million people in the twentieth century, although the last reported natural case was in Somalia in 1977.
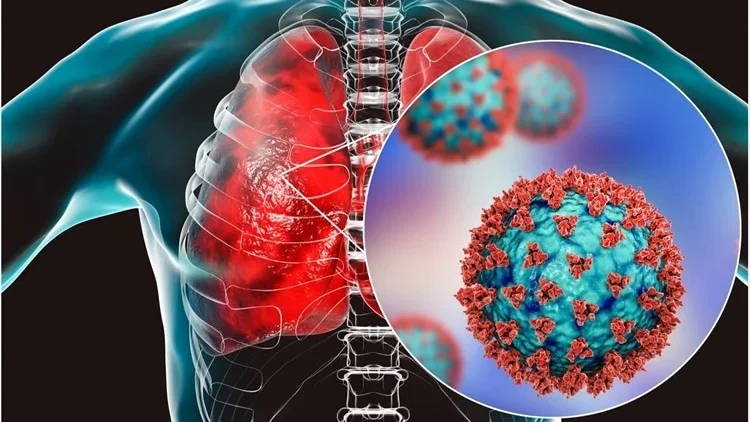
Overview
The first danger of coronavirus was experienced in the year 2003 when the SARS-CoV infected the global population.
Symptoms
High fever and muscle aches
Chest congestion and pneumonia
Fatality Rate
About 10 percent though the rate of mortality is higher among senior citizens.
Notable Outbreak
SARS that hit the world in 2003 affected more than 8400 people and led to 774 fatalities across the globe.
10. SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19 Virus)
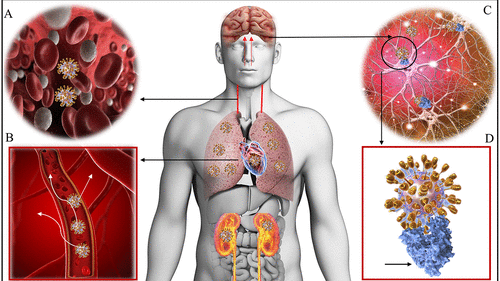
Overview
Since COVID-19 outbreak in late 2019 caused by Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), the world has changed beyond measure.
Symptoms
Fever, cough, and fatigue
Loss of taste and smell
Pneumonia and organ failure represents severe pneumonia disease.
Global Impact
Over 60 lakh deaths across the globe till 2024.
Interrupting economic, educational and health sectors
Prevention and Treatment
Pfizer, Moderna, AstraZeneca and others are vaccines.
These include; masking, social distance and all other protocals aimed at maintaining the sanctity of health among the populace.
Conclusion
These viruses underscore the enormous task that being presented by infectious diseases. Despite advancements in contemporary medicine the possibility of new and previously unrecognized virus as well as the reappearance of previously known ones still persist. Further commitment to respecting health, scientific, and educational sectors globally will require efforts to help prevent subsequent epidemics.
It is not just history that we must understand these deadly viruses – it is today and tomorrow that we need to prepare.
Source : Buzz Artical & HSUX Solutions
















