
In any working environment, the requirement of safety cannot be negotiated. In fact, the dangers of the industrial working environment may take a number of forms: from oil stains to electrical installations or bacteria. Some of them are used as safety directions and signals while others are utilized in signaling potential hazards that one has to avoid; all are an important part of a safety plan . It therefore requires everyone to be conversant with all these signs for them to embrace safe working as a culture as well as being able to avoid hazardous areas and equipment’s.
Contents
- 1 The Purpose of Hazard Symbols and Signs
- 2 Hazard Symbol Categories and Its Kinds
- 3 Decoding Common Workplace Hazard Symbols
- 4 Colours and shapes of signs
- 5 Proper Placement and Visibility of Signs
- 6 Making Employees Aware and Training Them
- 7 Common Mistakes and Misunderstandings
- 8 Legal and Compliance Requirements
- 9 Technology and Innovations in Hazard Signage
- 10 Conclusion
The Purpose of Hazard Symbols and Signs
Immediate Recognition: These visual recall signals provide implicit creativity to the workers about prospective hazards despite the fact that it may convey unfamiliar Marathi faith.
Legal Compliance: Employers are required by OSHA and ISO standards to use the symbols in premises to conform to legal requirements.
Prevention of Accidents: Hazard signs; when well posted and conspicuous help lower chances of accidents and or related incidents including deaths.
Promoting Awareness: It informs employees of probable dangers and makes them think carefully.
Hazard Symbol Categories and Its Kinds

This is because hazard symbols are grouped by the type of risk that they portray. Below are the main categories:
Physical Hazards
Physical hazard signs advise about risks that may lead to loss of life or damage to property. Examples include:
Flammable Materials: Represented by a flame icon.
Explosives: Symbolised by a bursting bomb that represents the typical sound of a bomb.
Electrical Hazards: Known by its symbol that comprises a lightning bolt in a triangle.
Chemical Hazards
Chemical symbols apply to a substance that can be hazardous in that the substance may be poisonous, caustic or flammable. Examples include:
Toxic Materials: Known with skeleton figure of two crosses.
Corrosive Substances: Symbolized by a drop of water dropping on a hand or a particular surface.
Oxidizing Agents: It is represented by a flame placed above a circle.
Biological Hazards
These symbols are used in healthcare, laboratories, and other environments where exposure to biological agents is possible:
Biohazard: Probably a circle composed of serpentine figures, where arcs intersect at the center.
Radiation Warning: Radioactive materials sign; A symbol in form of a three-lobed figure characteristic of radioactive materials.
Environmental Hazards
Environmental hazard symbols warn about substances that can harm ecosystems:
Aquatic Toxicity: Represented by a dead fish and tree.
Pollutants: Lights signaling chemical or a waste disposal hazard.
Decoding Common Workplace Hazard Symbols

It is important for every worker to know the widely used hazard symbols. Here are a few examples and their meanings:
Skull and Crossbones: Stands for ‘skull and crossbones’ meaning substances which are toxic if swallowed, inhaled or absorbed.
Flame: Refers to a substances which is evaporated, in liquid or gaseous or solid state and burns easily at the temperature it is in.
Exclamation Mark: Signals non-specific which include; Skin irritation, acute toxicity.
Corrosion: Is important if one will be working with materials that can harm the skin, eyes or metals.
Gas Cylinder: At points where reagents are kept under pressure namely gases that tend to burst when exposed to heat or in case of mechanical pressure.
Health Hazard: Shown symbolically as a figure with a star on the chest to illustrate long-term sickness, for instance, diseases of the lungs, or carcinogenicity.
Colours and shapes of signs
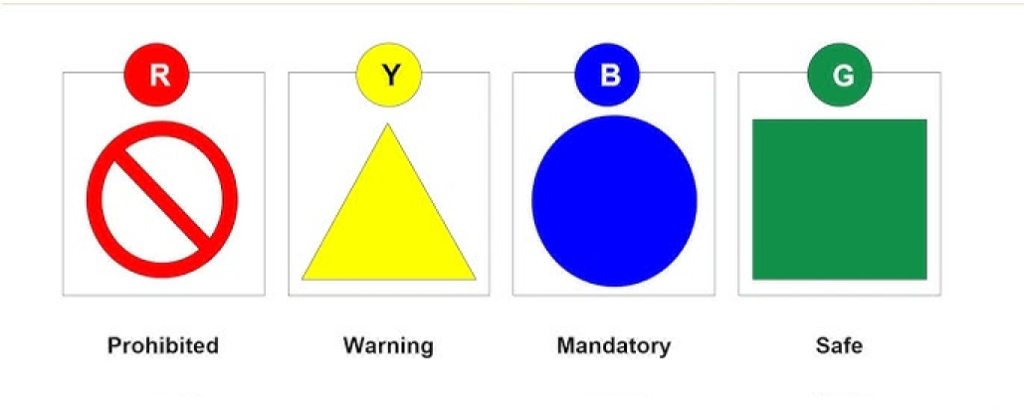
The design of hazard signs incorporates specific colors and shapes for easy identification:
Color Coding
Red: Signals prohibiting, warning or giving directions for emergencies (for instance the fire sign).
Yellow: For purpose of warning (like warning signs on the floor or any potential danger or risk).
Blue: Used to indicate that something must be done (for example, wearing protective equipment).
Green: Stands for safety messages, for example, exits, first aid or extinguishers.
Shapes of Signs
Circular: Mainly for directions and things that should be done.
Triangular: Informs the reader of danger or any danger sign.
Square/Rectangular: Has functional and decorative applications, particularly, for information signage.
Proper Placement and Visibility of Signs
To ensure their effectiveness, hazard symbols and signs must be strategically placed and clearly visible:
Placement: The signs should be placed close to the dangerous area, or around, for example over machines, next to a chemicals place, or at doors.
Visibility: Make sure that none of the created signs are obscured by different objects or are placed in poorly illuminated areas most of the time.
Size: The sizes of the signs also should depend on the distance at which the people are likely to read the signs.
Maintenance: Signage must be checked frequently to see that it is clean, not damaged and, most importantly, that it is easy to read.
Making Employees Aware and Training Them

The most compelling signs can be put up in a company yet employees may not grasp the meaning of the signs. Training is essential:
Orientation Programs: Teach Newcomers at workplace the various hazard symbols in use during initial orientation.
Regular Safety Drills: Students must repeat/strengthen what they already know through drills at times that mimic certain emergencies.
Interactive Tools: Adjust your approach as needed and utilize trending tools such as posters or creation of safety smartphone applications, e-learning safety modules.
Multilingual Signs: For population diversity in various workplaces, there should be multilingual signs and training materials.
Common Mistakes and Misunderstandings
Although they are pictographs, the basic forms of the hazard symbols can be confusing and manipulative at times. Here are common pitfalls to avoid:
Faded or Damaged Signs: Eventually the signs may begin to deteriorate and this causes confusion in the identification of the various brands.
Overloading with Signs: While a sign is meant to provide clear instruction or information, an employee can be overwhelmed by too many signs within his/her vista.
Ignoring Updates: They trigger concerns that current sign designs are unsafe due to their inability to meet existing standards.
Lack of Context: There are symbols which are further explained through texts alongside or pictogram signs.
Legal and Compliance Requirements
Adhering to legal standards is not just about avoiding fines; it’s about ensuring safety:
OSHA Standards: OSHA has regulations on the use of hazard signs for different activities, manufacturing construction and health care.
GHS Standards: The Globally Harmonized System (GHS) is a model for chemical classification and the associated label elements and pictograms accepted internationally.
ISO Guidelines: Even the most popular international code, the ISO 7010, outlines certain designs for the safety symbols to meet standardization.
Technology and Innovations in Hazard Signage
Advancements in technology have improved workplace safety signage:
Digital Signs: Smart boards can post dynamic safety messages and alerts since they are interactive.
Augmented Reality (AR): Smart-use allows employees to observe risks in the course of their working using AR tools.
QR Codes: Where posters can be placed include an embedded QR code that gives further information about how to implement the safety regulation.
Conclusion
Evidence thus indicates that by using hazard signs and symbols in the Workplace, the safety of the people will always be greatly enhanced. They pass abrupt information in the shortest time possible, and this reduces incidence of accidents and even loss of lives. Thus, organizations could design a safer environment by knowing the meanings, locations, and the regularity of their updates. Taking part in the safety of a workplace helps in avoiding all the possible hazards and making ergonomic an excellent aspect to work for; signage for awareness.
Source : Buzz Artical & HSUX Solutions















